Helicopter Training
Luxaviation Helicopters offers full training solutions, advanced type ratings up to and including instructor and examiner ratings. Our instructors all hold the highest grades of professional licence and have many years of both civilian and military flying experience, as well as extensive experience of flying in adverse weather conditions and challenging environments.
Flight Simulation
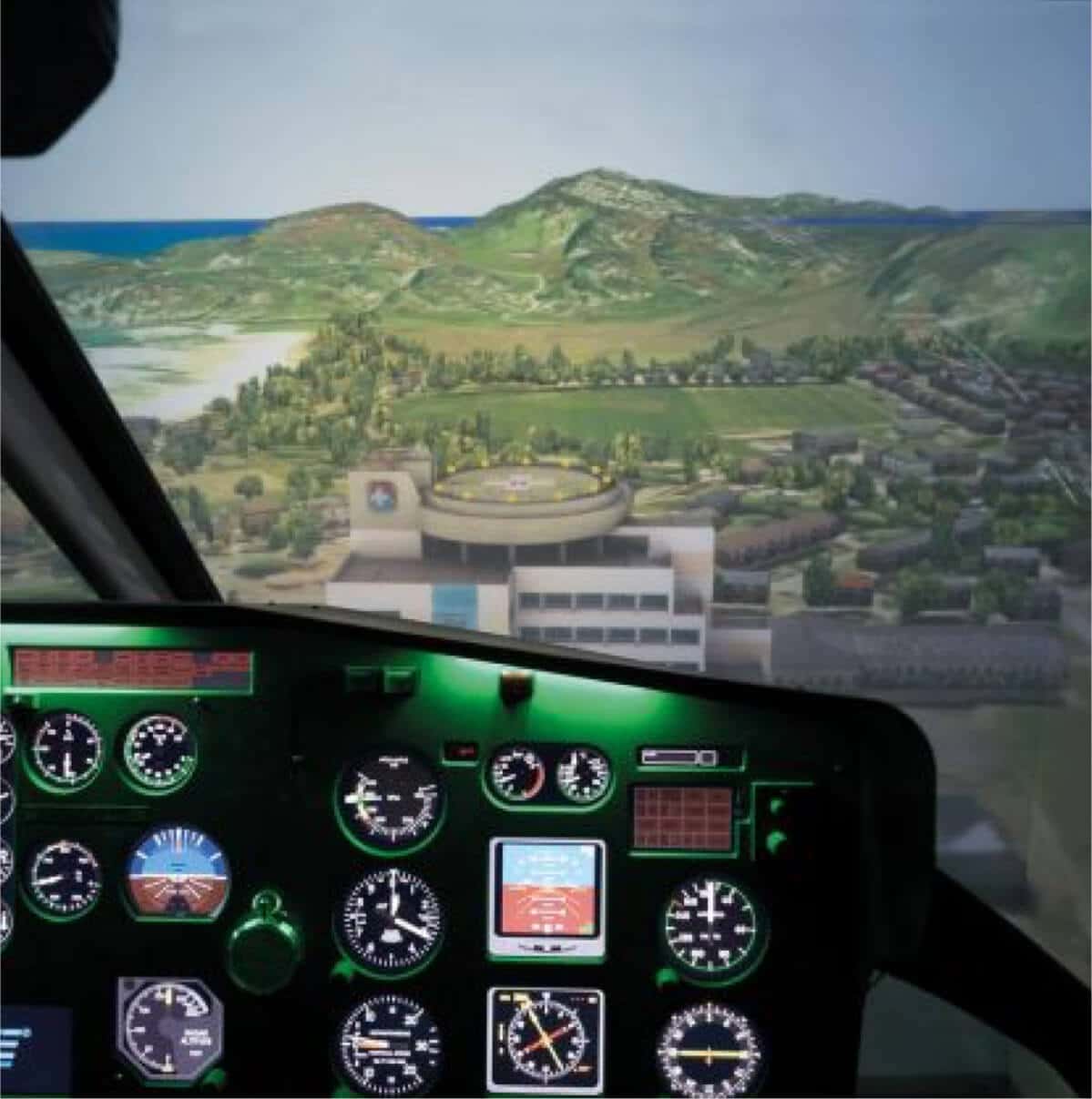
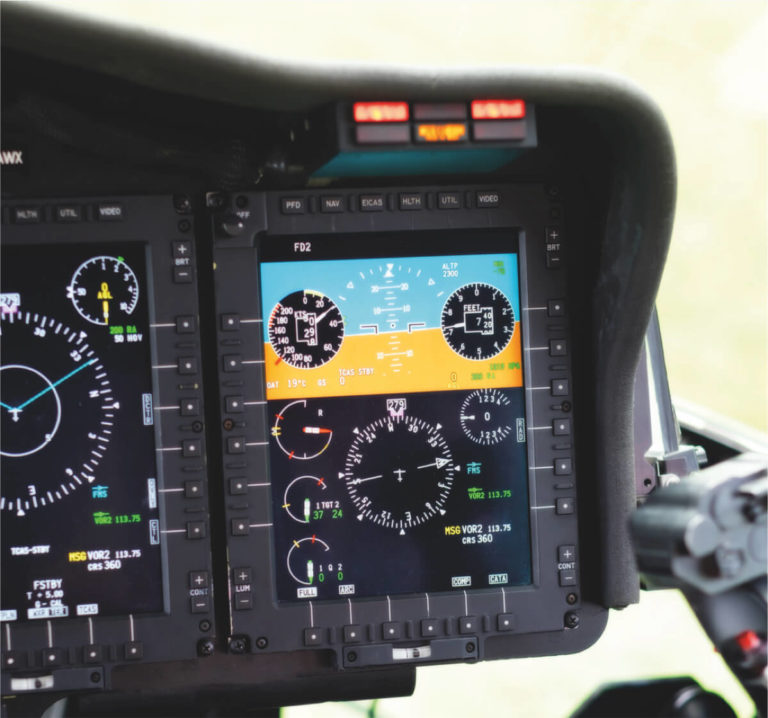
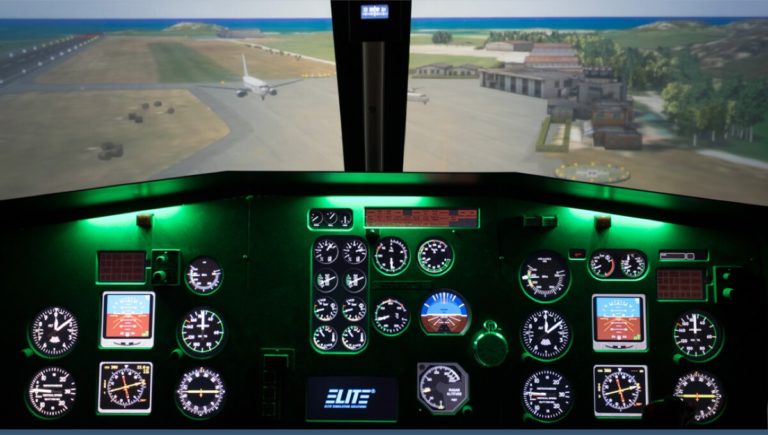
The Luxaviation synthetic training device is an Elite S623T FNPT II simulator based on the AS355 Twin Squirrel, holding CAA approvals issued in accordance with JAR-FSTD (H).
The simulator has dynamic control loading which includes a trim system with fully coupled autopilot functions, loading on the yaw pedals to simulate loss of hydraulic pressure, EFIS, intergrated Garmin 430 and weather modelling which includes rain, ice and snow.
Type Rating Training
Luxaviation can offer type rating training on the following aircraft:
- AS355
- AS365
- AW109
- AW139
- Bell 206
- Bell 429
- EC135
- EC145
- EC155
- S76
- SK76
IR(H) for civilian pilots
The Instrument Rating IR(H) is one of the most demanding courses in the civilian world. This rating for helicopters is now required for all commercial offshore operations and, increasingly, onshore helicopter activities in Europe. The course has been specifically set up with the AS 355 FNPT II at Kemble.
If you choose to come to Luxaviation for your training, you will be given access to all the Luxaviation training material via a Dropbox link prior to your arrival for pre-course study. During attendance of the course students are provided with an iPad for their personal use with all study material pre-loaded.
The simulator is available for free solo flying for all students, and remains so once a course is completed.
ICAO IR(H) - Part FCL IR(H) conversion
Important note: Your FAA or ICAO IR must be current and valid to allow credit from the full 50 hr course. Please contact the office if you need help regarding this.
This course comprises an extensive ground school package, followed by a minimum of 10 hours synthetic flight training in the FNPT and a minimum of 5 hours flight training in a multi engine IFR helicopter.
Qualified military pilots (QMP)
Luxaviation offers a variety of training courses for military pilots preparing their civilian licences. They include type ratings, instrument ratings and instructor ratings as well as the CPL(H) skills test and ATPL(H) training and skills test. We are happy to answer any questions you may have about entering civilian aviation and the conversion process but have outlined some basic facts below:
To fly in the civilian world you will need to convert your military IR to a civilian IR within 3 years of passing your exams. You will also need a type rating for a civilian aircraft. A military IR will exempt you from the full course, but your exemption will depend on what you hold.
MCC
The newest addition to Luxaviation’s training catalogue is the helicopter Multi Crew Cooperation course which is undertaken at the Kemble base in Gloucestershire.
The comprehensive eight-day course covers all elements of the EASA MCC course and teaches students to operate as an effective multi-pilot crew. Human Factors TKI, briefing, flying and debriefing relating to multi-crew operations are included in the syllabus. Students fly in both normal and abnormal situations, learning how to deal with emergencies inside and outside the cockpit.
PBN
As of August 2020 all helicopter pilots who hold an EASA IR will need to have a Performance-Based Navigation (PBN) qualification to continue flying IFR/IMC. This qualification allows pilots to fly PBN (GNSS) approaches and PBN routes.
Luxaviation now have the ability to provide complete PBN training in their FSTD at Kemble, including the PBN check/test. On successful completion of the course and check or test, the examiner has the authorisation to enter PBN into the IR holder’s licence which will allow them to exercise the privileges of this rating on any helicopter.
Allow 3 days for the course, which includes full ground school and 3 hours in the FSTD followed by the test. Ground school alone can also be provided if required.
Type rating instructor TRI(H)
The course can include the 'core course' of Teaching and Learning if a Flight Instructor (FI) rating is not held. Allow 8 days for the full TRI course, including this Teaching & Learning element, and 5 days for an add-TRI course. An initial TRI course requires 5 hours in the aircraft and the add-TRI requires 2 hours, followed by an Assessment of Competence undertaken by a Luxaviation examiner.
Type rating examiner TRE(H)
The applicant for a TRE(H) must have a minimum of 50 hours on the aircraft of choice before commencing this course.
TRE (VFR & IFR) standardisation courses, single & multi-engine, are available. The course duration is 1 week with an Assessment of Competence undertaken by the CAA on the aircraft of choice (this is booked by the candidate for a mutually convenient date). The course consists of ground school and 2 hours of flight training for TRE(V), or 4 hours of flight training for TRE(I).
Instrument rating instructor
The Instrument Rating Instructor IRI(H) course is designed to train the holder of a helicopter pilot's licence to conduct flight training for the issue of an IR(H).
UK CAA publications
UK CAA & EASA Publications, Forms, and Information
- CAP 804 Flight Crew Licensing: Mandatory Requirements, Policy and Guidance
- Confirmation of Military Experience for Military Accreditation Scheme
- Application for the Inclusion of an Instrument Rating in an EASA licence SRG 1161
- Application for the inclusion of a Type Rating in an EASA licence SRG 1173
- Application for an EASA licence
- Notes for the Guidance of Applicants taking the Initial Instrument Rating Skill Test (Helicopters) Stds Doc 01(H)
- RT Manual (CAP 413)
- EASA definitions
- EASA IR (H) requirements
Safety
Safety and the management of risk is the starting point, the middle and the end of all we do. Luxaviation has developed a mature safety management system over the last 12 years, not just because the regulations require it but because we firmly believe that it is an effective route to being ever better at what we offer.
A robust Safety Management System reduces costs, improves capability and gives people confidence.
Through its implementation we can achieve more and raise standards ever higher.